What is type safe compiler?
A type-safe compiler can do following feature:
- Validate type while compiling
- Compiled error if user try to assign wrong type
What is type safe compiler?
A type-safe compiler can do following feature:
Add assembly maven plugin
${project.artifactId}
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
repackage
maven-assembly-plugin
true
${project.basedir}/src/assembly/assembly.xml
create-archive
package
single

Producers create new messages. In other publish/subscribe systems, these may be called publishers or writers
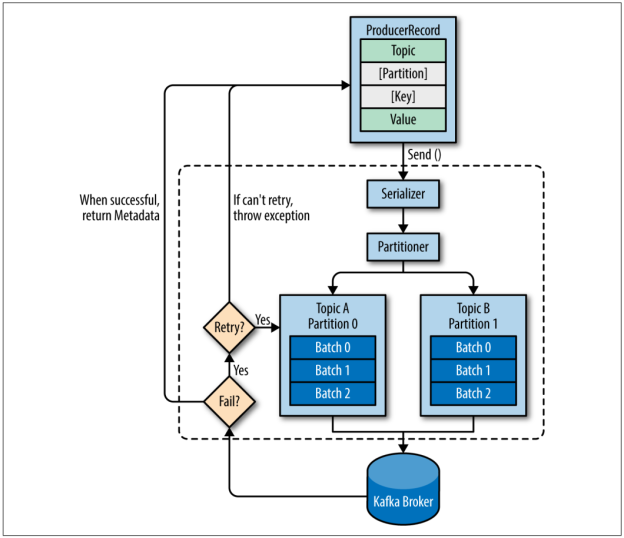
Producer concern flowing things:
Consumers read messages. In other publish/subscribe systems, these clients may be called subscribers or readers.
Kafka doesn’t track the acknowledgment from consumers the way many JMS queues do.
To consume message from Kafka we need to specify following parameters:
Each topic partition is only consumed by one consumer of a group
Number of consumer cannot be larger than number of partition

Handle following actions:
The action of updating current position in the partition is commit
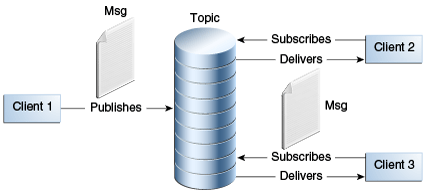
Messaging: a method to communicate between components
Loosely coupled: receiver doesn’t know anything about sender, and contrary the sender doesn’t know anything about the sender.

-- FUNCTION: public.table_update_notify()
-- DROP FUNCTION public.table_update_notify();
CREATE FUNCTION public.table_update_notify()
RETURNS trigger
LANGUAGE 'plpgsql'
COST 100
VOLATILE NOT LEAKPROOF
AS $BODY$
DECLARE
id bigint;
BEGIN
IF TG_OP = 'INSERT' OR TG_OP = 'UPDATE' THEN
id = NEW.id;
ELSE
id = OLD.id;
END IF;
PERFORM pg_notify('employee_channel', json_build_object('table', TG_TABLE_NAME, 'id', id, 'type', TG_OP)::text);
RETURN NEW;
END;
$BODY$;
ALTER FUNCTION public.table_update_notify()
OWNER TO postgres;
-- Trigger: employee_notify_update
-- DROP TRIGGER employee_notify_update ON production.employee;
CREATE TRIGGER employee_notify_update
BEFORE INSERT OR DELETE OR UPDATE
ON production.employee
FOR EACH ROW
EXECUTE PROCEDURE public.table_update_notify();
Now every time, table employee changed, it fire an event with payload is information of the change
1. Sử dụng properties file SpringApplication sẽ load các property từ tất cả các file application.properties trong các vị trí sau, và thêm chúng vào application environment: + Folder /config bên trong folder hiện tại. + Folder hiện tại. + Class path /config + Root class path Mặc định, SpringApplication sẽ load theo thứ tự từ dưới lên trên. Và các property nào load sau sẽ override property load trước. Vì lý do này, bạn cứ đặt property vào class path bình thường, khi muốn config ngoài file jar, thì sẽ đặt file application.properties vào folder /config là được. Như vậy cần phải build dự án với maven sao cho có kết quả trong folder target như sau:
+-target
+---myapp.jar
+---config
+--application.properties

1. Sử dụng class Configuration
Spring Boot ưu ái việc sử dụng các class Configuration. Mặc dù bạn có thể hoàn toàn sử dụng việc gọi hàm SpringApplication.run() ngay bên trong file XML, nhưng nhìn chung Spring khuyên điểm xuất phát của ứng dụng là một class với annotation @Configuration. Thông thường thì class với hàm main() thì nên là cũng là lớp chứa @Configuration.
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class Application
{
public static void main(final String[] args)
{
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}